What Is Shared Hosting?
What Is Shared Hosting?
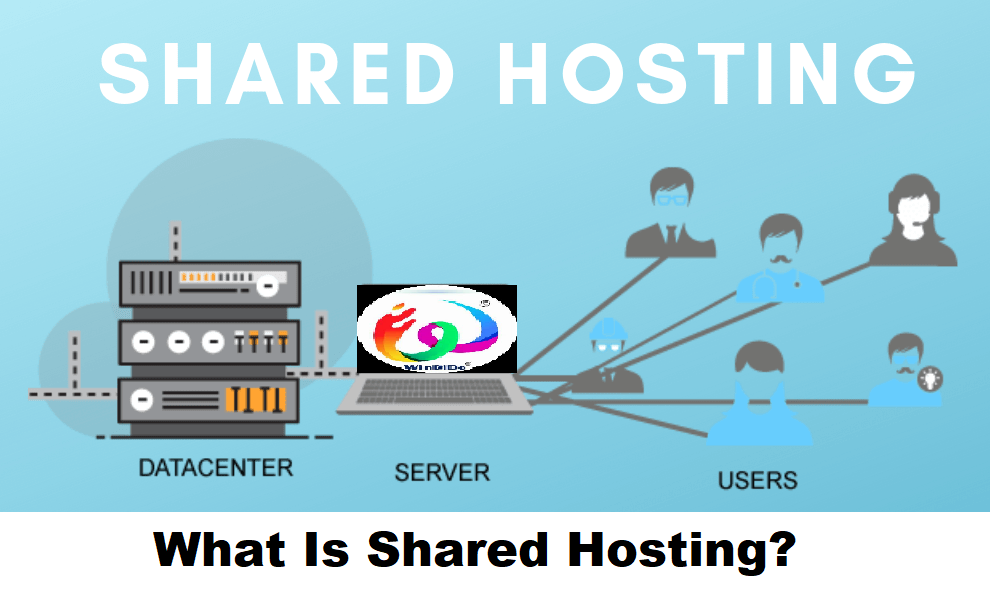
Shared hosting is a type of web hosting service where multiple websites are hosted on a single server. In this setup, the server’s resources, such as processing power, memory, and disk space, are shared among multiple users or customers. Each user gets a portion of the server’s resources for their website.
Here are some key characteristics of shared hosting:
- Cost-Effective: Shared hosting is typically more affordable than other hosting options because the costs are distributed among multiple users.
- Ease of Use: Shared hosting providers often offer user-friendly interfaces and control panels, making it easy for users to manage their websites without requiring advanced technical skills.
- Limited Resources: Since resources are shared, the performance of your website may be affected by the activities of other users on the same server. If one website experiences a sudden spike in traffic or consumes a significant amount of resources, it can potentially impact the performance of other websites on the server.
- Less Control: Users have limited control over server settings and configurations compared to other hosting options like VPS (Virtual Private Server) or dedicated hosting.
- Suitable for Small Websites: Shared hosting is generally suitable for small to medium-sized websites with moderate traffic. It may not be the best choice for large, high-traffic websites or those with specific performance and customization requirements.
- Managed Services: Shared hosting is often managed by the hosting provider, which means they take care of server maintenance, security, and other technical aspects. Users can focus on managing their websites without worrying about server management.
Advantages of Shared Hosting:
Shared hosting offers several advantages, especially for individuals and small businesses with modest website requirements. Here are some key advantages of shared hosting:
- Cost-Effectiveness: Shared hosting is one of the most affordable hosting options available. The cost is distributed among multiple users sharing the same server, making it an economical choice for those on a budget.
- Ease of Use: Shared hosting providers often offer user-friendly control panels and interfaces, making it easy for individuals with limited technical expertise to manage their websites, domains, and email accounts.
- Quick Setup: Shared hosting plans typically come with pre-configured settings, allowing users to quickly set up their websites without the need for extensive technical knowledge. This is beneficial for those who want to get their websites up and running swiftly.
- Managed Services: Shared hosting providers usually handle server maintenance tasks, security updates, and technical issues. This allows users to focus on building and maintaining their websites without having to worry about the backend server management.
- Scalability: Shared hosting plans often come with the option to upgrade to higher-tier plans or switch to more advanced hosting solutions as the website grows. This scalability is useful for businesses that anticipate increasing their online presence over time.
- Technical Support: Shared hosting providers typically offer customer support to assist users with technical issues or inquiries. This can be valuable, especially for users who are not well-versed in server management or troubleshooting.
- Resource Efficiency: For small to medium-sized websites with moderate traffic, shared hosting can provide sufficient resources. Users share server resources like CPU, memory, and disk space, making it a suitable option for websites that do not require a dedicated server.
- Ideal for Beginners: Shared hosting is an excellent choice for beginners and those launching their first websites. It allows users to learn about website management without the complexities associated with more advanced hosting options.
Disadvantages of Shared Hosting:
- Limited Resources: Shared hosting involves sharing server resources with multiple users. If one website on the server experiences a sudden spike in traffic or consumes excessive resources, it can affect the performance of other websites on the same server. This can lead to slower loading times and reduced overall performance.
- Security Concerns: Security is a shared responsibility in shared hosting. If one website on the server is vulnerable to security threats, it may pose risks to other websites as well. While hosting providers implement security measures, the actions of other users can impact the overall security of the server.
- Less Control: Users have limited control over server configurations and settings in shared hosting environments. Customizations may be restricted, making it challenging for users with specific technical requirements or those who need to install custom software.
- Potential for Downtime: Since multiple websites share the same server resources, any issues affecting the server, such as maintenance or technical problems, can lead to downtime for all hosted websites. While reputable hosting providers strive to minimize downtime, it’s a risk inherent in shared hosting.
- Performance Variability: The performance of your website can be influenced by the activities of other users on the same server. If a neighboring website experiences high traffic or resource usage, it may impact the speed and responsiveness of your site.
- Not Suitable for High-Traffic Sites: Shared hosting is generally not ideal for large websites with high traffic volumes or resource-intensive applications. Such websites may experience performance bottlenecks and may need more dedicated resources offered by other hosting options like VPS or dedicated servers.
- Limited Software Options: Shared hosting providers often impose restrictions on the types of software and applications that can be installed on the server. This limitation can be a challenge for users with specific software requirements.
- Email Deliverability Issues: Shared hosting environments may face email deliverability issues, especially if one or more users on the server engage in spammy activities. This can affect the reputation of the shared IP address, potentially leading to email delivery problems for all users on the server.
Alternatives to Shared Hosting:
There are several alternatives to shared hosting, each catering to different needs and requirements. Here are some common alternatives:
- Virtual Private Server (VPS) Hosting:
- VPS hosting provides more dedicated resources compared to shared hosting. In a VPS environment, a physical server is divided into multiple virtual servers, each with its own dedicated resources. This offers more control and better performance compared to shared hosting.
- Dedicated Hosting:
- With dedicated hosting, you have an entire physical server dedicated exclusively to your website. This option provides maximum control over server configurations, resources, and security. Dedicated hosting is suitable for high-traffic websites or applications with specific resource requirements.
- Cloud Hosting:
- Cloud hosting utilizes a network of virtual servers across multiple physical machines. It offers scalability, flexibility, and reliability as resources can be easily scaled up or down based on demand. Cloud hosting is suitable for websites with varying traffic levels.
- WordPress Hosting:
- WordPress hosting is specifically optimized for websites built on the WordPress platform. It often includes features like automatic WordPress updates, specialized caching, and security enhancements tailored for WordPress sites.
- Managed Hosting:
- Managed hosting providers take care of server management tasks, security, and technical aspects, allowing users to focus solely on managing their websites. This can be available for various hosting types, including VPS and dedicated hosting.
- Reseller Hosting:
- Reseller hosting allows users to become hosting providers themselves by reselling hosting services. This is suitable for individuals or businesses that want to offer hosting services to others without managing the infrastructure.
- Colocation Hosting:
- Colocation hosting involves renting space in a data center to house your own server hardware. You have complete control over the server, including hardware configurations, and the data center provides the necessary infrastructure and connectivity.
- Clustered Hosting:
- Clustered hosting involves distributing website resources across multiple servers to enhance reliability and performance. This setup is designed to minimize downtime and provide redundancy in case one server fails.
- Enterprise Hosting Solutions:
- Large enterprises with complex hosting needs may opt for customized hosting solutions tailored to their specific requirements. This can include a combination of dedicated servers, cloud services, and other infrastructure components.
What Does Shared Hosting Mean?
Shared hosting refers to a web hosting arrangement in which multiple websites are hosted on the same server. In this setup, the server’s resources, including processing power, memory, and disk space, are shared among multiple users or customers. Each user gets a portion of the server’s resources to host their website.
Here’s a breakdown of the key aspects of shared hosting:
- Shared Resources: The server resources are shared among various users. This includes the central processing unit (CPU), random access memory (RAM), storage space, and bandwidth. Websites hosted on the same server compete for these resources.
- Cost-Effective: Shared hosting is typically more affordable than other hosting options because the costs are distributed among multiple users. It’s a cost-effective solution for individuals, small businesses, or those who are just starting with a website.
- Ease of Use: Shared hosting providers often offer user-friendly control panels and interfaces, making it easy for users to manage their websites, domains, and email accounts. This is particularly beneficial for those who may not have advanced technical skills.
- Managed Services: Shared hosting is often managed by the hosting provider. This means that tasks such as server maintenance, security updates, and technical support are handled by the hosting company, allowing users to focus on managing their websites.
- Limited Control: Users have limited control over server settings and configurations compared to other hosting options like Virtual Private Server (VPS) or dedicated hosting. Customizations may be restricted to ensure the stability of the shared environment.
- Scalability: Shared hosting is suitable for small to medium-sized websites with moderate traffic. However, if a website outgrows the resources provided by shared hosting, users may need to consider upgrading to a more advanced hosting solution.
- Security Considerations: While hosting providers implement security measures, the security of shared hosting can be influenced by the actions of other users on the same server. It’s crucial for users to follow best security practices to protect their websites.
Techopedia explains Shared Hosting:
Techopedia defines shared hosting as a type of web hosting where multiple websites share resources on the same server. In a shared hosting environment, each website has its own partitioned space on the server, but they all use the same server resources, including the same CPU, RAM, and disk storage. This hosting model is cost-effective because the expenses associated with the server are distributed among multiple users.
Here are some key points covered in Techopedia’s explanation of shared hosting:
- Resource Sharing: Shared hosting involves multiple users sharing the resources of a single server. This includes the server’s processing power, memory, storage, and bandwidth.
- Cost-Effective Solution: Shared hosting is considered a cost-effective hosting option. Since the server costs are shared among multiple users, each user pays a relatively lower fee compared to hosting on a dedicated server.
- Ease of Use: Shared hosting is often designed to be user-friendly. Hosting providers typically offer easy-to-use control panels and interfaces that allow users to manage their websites without requiring advanced technical skills.
- Managed Services: Hosting providers usually manage the server, taking care of tasks such as maintenance, security updates, and support. This allows users to focus on building and maintaining their websites rather than dealing with server administration.
- Limited Control: Users have limited control over the server’s settings and configurations. This limitation helps ensure the stability and security of the shared environment but may restrict certain customization options.
- Scalability Challenges: While shared hosting is suitable for small to medium-sized websites, it may have limitations when it comes to scalability. As a website grows and requires more resources, users may need to consider other hosting options like Virtual Private Servers (VPS) or dedicated hosting.
- Security Considerations: Security is a shared responsibility in a shared hosting environment. The actions of one user can potentially impact the security of other users on the same server. Therefore, users need to follow best practices to secure their individual accounts.
How does shared hosting work?
Shared hosting works by hosting multiple websites on a single physical server and sharing its resources among all the hosted websites. Here’s an overview of how shared hosting operates:
- Server Setup:
- A hosting provider sets up a powerful server with a specific configuration that includes a certain amount of CPU power, RAM, storage space, and network bandwidth.
- This server is equipped with a web server software (such as Apache or Nginx), a database server (such as MySQL or PostgreSQL), and other necessary components.
- Partitioning Resources:
- The server’s resources are partitioned or divided into smaller portions, and each portion is allocated to a different user or hosting account.
- Each user’s hosting account includes a separate directory on the server where they can store their website files, databases, and other data.
- Hosting Multiple Websites:
- Multiple users sign up for shared hosting plans, and each user’s website is hosted within its designated space on the server.
- Users on shared hosting share the same server IP address.
- Control Panel Access:
- Hosting providers typically offer a control panel (such as cPanel or Plesk) that allows users to manage their websites, domains, email accounts, and other hosting settings.
- Users can use the control panel to upload files, create databases, set up email accounts, and perform other tasks related to managing their websites.
- Resource Sharing:
- The server’s resources, including CPU, RAM, and storage, are shared among all the hosted websites. Each website gets a portion of these resources.
- Since resources are shared, the performance of one website can potentially be affected by the activities of other websites on the same server.
- Web Server Handling Requests:
- When a visitor accesses a website hosted on the shared server, the web server receives the request and processes it.
- The server retrieves the requested web page or content from the appropriate user’s directory and sends it to the visitor’s browser.
- Managed Services:
- The hosting provider is responsible for managing the server, performing routine maintenance tasks, applying security updates, and addressing technical issues.
- Users do not need to worry about the backend server management, as it is taken care of by the hosting company.
- Security Measures:
- Hosting providers implement security measures to isolate user accounts and protect against potential security threats. However, users are also responsible for securing their individual accounts.
FAQ’s
- What is shared hosting?
- Shared hosting is a type of web hosting where multiple websites share resources on the same server. Each user has a portion of the server’s resources to host their website.
- How does shared hosting work?
- Shared hosting works by hosting multiple websites on a single server and dividing the server’s resources among the hosted websites. Users share the same server IP address and have access to a control panel to manage their websites.
- What are the advantages of shared hosting?
- Advantages of shared hosting include cost-effectiveness, ease of use, quick setup, managed services, and scalability for small to medium-sized websites.
- What are the disadvantages of shared hosting?
- Disadvantages include limited resources, potential for performance issues due to resource sharing, security concerns, limited control over server settings, and potential email deliverability issues.
- Is shared hosting suitable for my website?
- Shared hosting is suitable for individuals, small businesses, and websites with moderate traffic. It’s a good option for those on a budget and who don’t require dedicated resources.
- Can I upgrade from shared hosting to another hosting type?
- Yes, many hosting providers offer the option to upgrade to Virtual Private Server (VPS), dedicated hosting, or other advanced hosting solutions as your website grows and requires more resources.
- How is security handled in shared hosting?
- Hosting providers implement security measures to isolate user accounts and protect against common threats. However, users also play a role in securing their individual accounts and websites.
- What is the difference between shared hosting and VPS hosting?
- In shared hosting, multiple users share the same server resources, while VPS hosting provides a virtualized environment with dedicated resources for each user. VPS offers more control and scalability but is generally more expensive than shared hosting.
- Can I install custom software on a shared hosting server?
- Shared hosting providers may restrict the installation of certain custom software to maintain the stability of the shared environment. Users should check with their hosting provider for specific policies.
- What happens if another website on the shared server experiences high traffic?
- If another website on the shared server experiences a traffic spike, it may potentially impact the performance of other websites on the server. However, reputable hosting providers implement measures to mitigate such issues.
- How do I choose a shared hosting provider?
- Consider factors such as server reliability, customer support, features offered, scalability options, and user reviews when choosing a shared hosting provider.
#entrepreneurship #follow #love #photography #affiliatemarketing #businessowner #webdevelopment #content #like #art #b #emailmarketing #fashion #instagood #websitedesign #google #digitalmarketingstrategy #marketingonline #socialmediamanager #searchengineoptimization #facebook #digitalmarketer #empreendedorismo #workfromhome #copywriting #instagrammarketing #digitalagency #brand #digitalmarketingexpert #windido.

Leave a Reply